| |
|
GOES, POES, & MetOp Weather Satellites
|
The U.S. National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) operates various weather satellites. Some of the satellites are geostationary (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites, or GOES), and others are in polar low Earth orbits (Polar Orbiting Environmental Satellites, or POES).
The first of the next-generation polar-orbiting satellites, known as Suomi NPP (National Polar-orbiting Partnership), was launched on October 28th, 2011. An additional next-gen satellite launch is scheduled for 2017.
As a result of the 2012 Middle Class Tax Relief and Jobs Creation Act, POES, GOES, and MetOp satellites use some spectrum that is shared by, or adjacent to, the 1695-1710 MHz portion of the AWS-3 spectrum. This segment is used for uplinks from mobile devices to base stations. To mitigate interference to NOAA operations, the government has issued an RFP for an RF Interference Management System (RFIMS), which will be installed at the 17 official NOAA ground stations, listen for interference, and alert mobile network operators in real time that mitigation measures are needed. The RFIMS concept was first proposed by the Commerce Spectrum Management Advisory Committee (CSMAC).
Details of the signals transmitted by the satellites are provided in the linked presentation.
According to NOAA:
NOAA’s most sophisticated Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES), known as the GOES-R Series, provide advanced imagery and atmospheric measurements of Earth’s Western Hemisphere, real-time mapping of lightning activity, and improved monitoring of solar activity and space weather.
GOES satellites orbit 22,236 miles above Earth’s equator, at speeds equal to the Earth's rotation. This allows them to maintain their positions over specific geographic regions so they can provide continuous coverage of that area over time.
The first satellite in the series, GOES-R, now known as GOES-16, was launched in 2016 and is currently operational as NOAA’s GOES East satellite. GOES-S, now known as GOES-17, was launched in 2018 and now serves as an on-orbit backup. GOES-T, now GOES-18, launched in 2022 and now serves as NOAA’s operational GOES West satellite. GOES satellites are designated with a letter prior to launch. Once a GOES satellite has successfully reached geostationary orbit, it is renamed with a number. GOES-U, the final satellite in the series, is scheduled to launch in 2024.
Together, GOES East and GOES West watch over more than half the globe — from the west coast of Africa to New Zealand and from near the Arctic Circle to the Antarctic Circle.
The GOES-R Program is a collaborative effort between NOAA and NASA. NASA builds and launches the satellites for NOAA, which operates them and distributes their data to users worldwide.
The Polar Operational Environmental Satellites (POES) satellite system makes 14 nearly polar orbits per day approximately 520 miles above Earth. The Earth's rotation allows the satellite to see a different view with each orbit, and each satellite provides two complete views of weather around the world each day. NOAA partners with the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) to operate two polar-orbiting satellites – one POES and one European polar-orbiting satellite called MetOp.
The POES instruments include the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer, the Advanced TIROS Operational Vertical Sounder (ATOVS), and the Microwave Humidity Sounder provided by EUMETSAT. These instruments provide visible, infrared, and microwave data which is used for a variety of applications such as to monitor cloud and precipitation, determine surface properties, and profile humidity.
Data from the POES supports a broad range of environmental monitoring applications including weather analysis and forecasting, climate research and prediction, global sea surface temperature measurements, atmospheric soundings of temperature and humidity, ocean dynamics research, volcanic eruption monitoring, forest fire detection, global vegetation analysis, and search and rescue.
|
Frequencies |
| Frequency | Bandwidth | Use | Service | Table |
| 137.1 MHz | 34 kHz | POES Automatic Picture Transmission (APT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 137.5 MHz | 34 kHz | POES Automatic Picture Transmission (APT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 137.62 MHz | 34 kHz | POES Automatic Picture Transmission (APT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 137.9125 MHz | 34 kHz | POES Automatic Picture Transmission (APT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1676 MHz | 5.2 MHz | Legacy GOES SDL downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1680 MHz | 475 kHz | GOES-R DCPR downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1681.5 MHz | 400 kHz | Legacy GOES MDL downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1685.7 MHz | 4.22 MHz | Legacy GOES GVAR downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1686.6 MHz | 10.9 MHz | GOES-R GRB downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1691 MHz | 586 kHz | Legacy GOES LRIT downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1692.7 MHz | 27 kHz | Legacy GOES EMWIN-N downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1693 MHz | 80 kHz | GOES-R CDA telemetry downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1694 MHz | 16 kHz | Legacy GOES CDA Telemetry downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1694.1 MHz | 1.205 MHz | GOES-R HRIT downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1694.5 MHz | 475 kHz | Legacy GOES DCPR downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1694.8 MHz | 475 kHz | Legacy GOES DCPR downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1698 MHz | 5.32 MHz | POES Local Area Coverage (LAC) and Global Area Coverage (GAC) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1698 MHz | 2.66 MHz | POES High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1701.3 MHz | 4.5 MHz | MetOp Advanced High Resolution Picture Transmissions (AHRPT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1702.5 MHz | 5.32 MHz | POES Local Area Coverage (LAC) and Global Area Coverage (GAC) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1702.5 MHz | 2.66 MHz | POES High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1707 MHz | 5.32 MHz | POES Local Area Coverage (LAC) and Global Area Coverage (GAC) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1707 MHz | 4.5 MHz | MetOp Advanced High Resolution Picture Transmissions (AHRPT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1707 MHz | 12 MHz | Suomi NPP Low Data Rate (LDR) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 1707 MHz | 2.66 MHz | POES High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
| 7812 MHz | 30 MHz | Suomi NPP High Data Rate (HDR) downlink | Meteorological-satellite | F |
External Links:
Associated Files:
| | DySpan_presentation_v2
Radio Frequency Interference Monitoring System for Weather Satellite Ground Stations: Challenges and Opportunities, presentation by NOAA at the DySPAN 2017 conf...
|
| |
Display this entry in a page by itself
Edit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Defense Satellite Communication System 3 (DSCS III)
|
According to the U.S. Space Force:
Defense Satellite Communications System (DSCS) constellation provides long haul communications to users worldwide through contested environments.
DSCS supports: the defense communications system, the military’s ground mobile forces, airborne terminals, ships at sea, and Department of Defense (DOD).
The first DSCS III satellite was launched in October 1982. The final DSCS III satellite, B6, was launched in August 2003. In all, DSCS III successfully launched 14 satellites, six of which are still operational and continue to be used in various capacities, from operational communications in Southwest Asia to research and development of ground-based support capabilities.
Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC), Los Angeles Air Force Base, Calif., sustains the DSCS Space Segment contract.
DSCS III satellites support globally distributed DOD and national security users. Modifications made to these satellites will provide substantial capacity improvements through higher power amplifiers, more sensitive receivers, and additional antenna connectivity options. The DSCS communications payload includes six independent Super High Frequency (SHF) transponder channels. Three receive and five transmit antennas provide selectable options for Earth coverage, area coverage and/or spot beam coverage. A special purpose single-channel transponder is also on board.
DSCS satellites provide the capabilities needed for effective implementation of worldwide military communications. It can adapt rapidly to dynamic operating conditions and perform under stressed environments. DSCS operates with large or small terminals. DSCS’s independent channels group users by operational needs or geographical location by allocating receiver sensitivity and transmitter power, thus providing maximum efficiency.
|
Paired Frequency Bands |
| Paired Bands | Use | Service | Table |
| 7250 - 7750 MHz | DSCS III downlink | Mobile-satellite | F |
| 7900 - 8400 MHz | DSCS III uplink | Mobile-satellite | F |
Frequencies |
| Frequency | Bandwidth | Use | Service | Table |
| 7600 MHz | - | DSCS III Beacon (A series satellites) | Mobile-satellite | F |
| 7604.705882 MHz | - | DSCS III Beacon (B series satellites) | Mobile-satellite | F |
| 8005.146484 MHz | - | DSCS III Channel 1 command uplink | Mobile-satellite | F |
| 8370.146484 MHz | - | DSCS III Channel 5 command uplink | Mobile-satellite | F |
External Links:
Display this entry in a page by itself
Edit
|
|
|
|
|
|
IEEE 802.15.4 HRP UWB
|
High pulse repetition frequency ultra-wideband (HPR UWB) is one of the physical layers defined for low data rate personal area network (LR-WPAN) communications in the IEEE 802.15.4 standard.
According to the FiRa Consortium:
"In challenging environments, such as parking structures, hospitals, airports and high density venues, ultra-wideband (UWB) technology outperforms other technologies in terms of accuracy, power consumption, robustness in wireless connectivity, and security, by a wide margin.
"UWB securely determines the relative position of peer devices with a very high degree of accuracy and can operate with line of sight at up to 200 meters. In contrast to narrow band wireless technologies, the use of wide bandwidth means UWB provides very stable connectivity, with little to no interference and offers highly precise positioning, even in congested multi-path signal environments.
"By calculating precise location, fine ranging based on UWB is a more secure approach to closing and opening locks, whether those locks are installed on a car door, a warehouse entryway, a conference room, or your front door."
|
Frequencies |
| Frequency | Bandwidth | Use | Service | Table |
| 499.2 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 0 | - | - |
| 3494.4 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 1 | - | - |
| 3993.6 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 2 | - | - |
| 3993.6 MHz | 1.3312 GHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 4 | - | - |
| 4492.8 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 3 | - | - |
| 6489.6 MHz | 1.0816 GHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 7 | - | - |
| 6489.6 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 5 | - | - |
| 6988.8 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 6 | - | - |
| 7488 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 8 | - | - |
| 7987.2 MHz | 1.3312 GHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 11 | - | - |
| 7987.2 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 9 | - | - |
| 8486.4 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 10 | - | - |
| 8985.6 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 12 | - | - |
| 9484.8 MHz | 1.35497 GHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 15 | - | - |
| 9484.8 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 13 | - | - |
| 9984 MHz | 499.2 MHz | 802.15.4 HRP UWB Channel 14 | - | - |
External Links:
Associated Files:
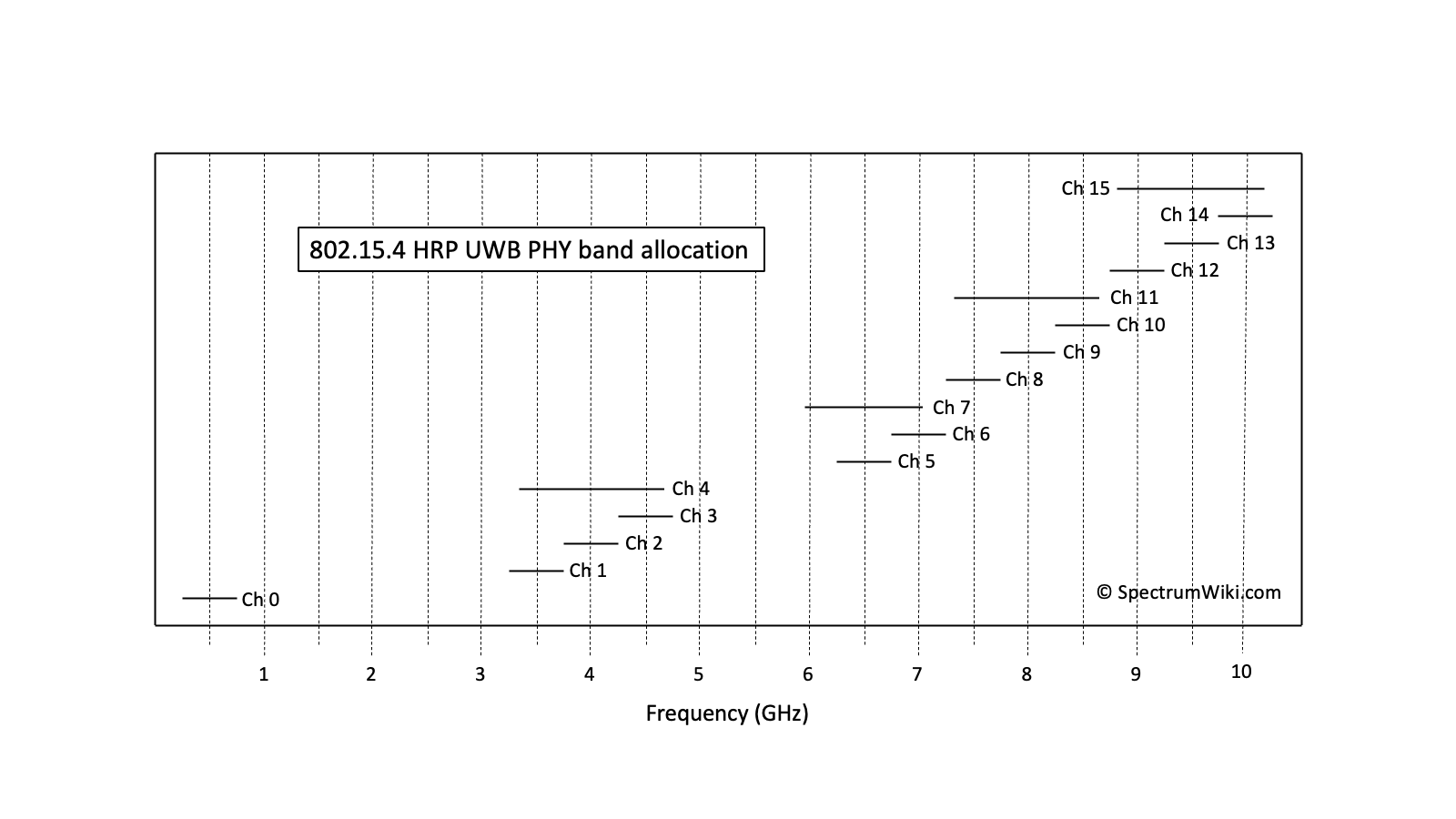
802.15.4 HRP UWB PHY band allocation
Display this entry in a page by itself
Edit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|